ViTLearn: Vision-text for Robot Learning using LLMs
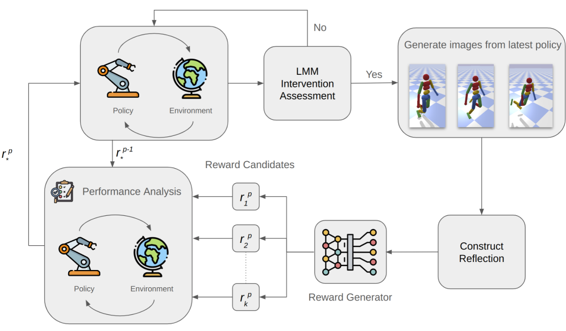
Natural language is a fundamental component in the development of robotic algorithms, enabling effective human-robot dialogue and guiding reinforcement learning processes. While reinforcement learning facilitates complex behaviours, optimally modelling rewards remains a significant challenge. Large Language Models like ChatGPT excel in following instructions, but the potential of Large Multi-Modal Models (LMMs), which integrate visual and textual inputs, is underexplored. This paper proposes ViTLearn, a LMM-Reinforcement Learning framework that leverages both vision and language to shape rewards and enable more complex robotic behaviours. Incorporating visual inputs is crucial for tasks that are difficult to articulate with words alone, as it can enhance task comprehension and performance. By fusing vision and language, ViTLearn aims to advance robotic learning and behaviour optimisation, promoting more intuitive human-robot interactions.
This project was conducted in collaboration with the CSIRO Robotic Perception and Autonomy Group.
Poster
🖼️ view the poster for ViTLearn: Vision-text for Robot Learning using LLMs!Prize Categories

Best Software Project
Technologies and Skills
- Deep reinforcement learning
- Robotics
- Large language models
- Large multimodal models